kimchi history
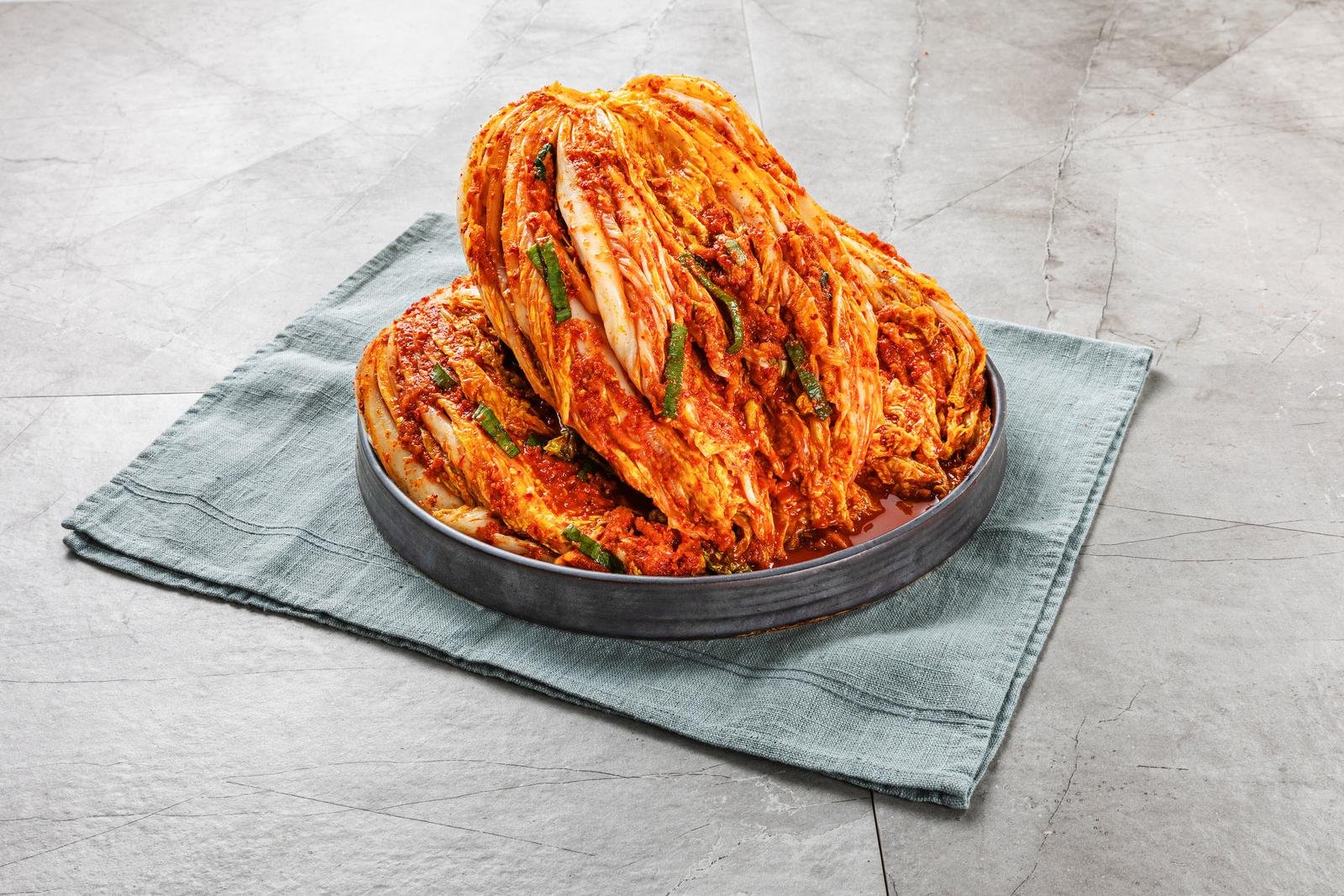

Kimchi, a traditional Korean dish, holds a significant place in Korean cuisine and culture. Its history is deeply rooted in Korean heritage, stretching back thousands of years. This simple and extensive overview will delve into the key subject of kimchi history, shedding light on its origins, evolution, and cultural significance.
The origins of kimchi can be traced back to ancient times, around 3,000 years ago in the Korean Peninsula. The earliest records of its existence are found in Samguk Sagi, a historical document from the 12th century, which describes the practice of fermenting and preserving vegetables with salt. However, it is believed that Koreans have been preserving food through fermentation long before these written accounts.
Originally, kimchi was not the vibrant, spicy dish that it is today. Early versions of kimchi consisted of mainly salted vegetables, such as radishes and cabbage, which were stored in traditional Korean earthenware called onggi. This process allowed vegetables to ferment slowly over time, providing essential nutrients and probiotics during harsh winters when fresh vegetables were scarce.
The modern kimchi we know today took shape during the Joseon Dynasty in the 15th century. Chili peppers, introduced to Korea by Portuguese traders, were incorporated into the kimchi recipe, which transformed it into the spicy and pungent delicacy we know today. This addition not only enhanced the flavor but also had antimicrobial properties, further aiding in the preservation process.
Kimchi became an integral part of Korean cuisine and culture, transcending its role as a mere side dish. It symbolized Korea's ingenuity in utilizing local ingredients, promoting sustainability, and preserving food during long winters. Kimchi-making became a communal activity, bringing families and communities together during the preparation process. This tradition continues to this day during the annual kimjang festival, where families come together to prepare and store large quantities of kimchi for the winter.
Over time, kimchi has expanded its variations and ingredients. Along with the traditional cabbage kimchi (baechu kimchi), there are countless regional and seasonal variations, such as radish kimchi (kkakdugi), water kimchi (mul kimchi), cucumber kimchi (oi kimchi), and many more. Each variation carries unique flavors and textures, reflecting the local ingredients available.
Not limited to its culinary significance, kimchi has garnered global recognition for its health benefits. The fermentation process involved in making kimchi produces lactic acid bacteria, beneficial for digestion and maintaining a healthy gut flora. It is rich in vitamins A, B, and C, and provides a significant source of dietary fiber. The various spices and ingredients contribute to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
With the rising popularity of Korean cuisine around the world, kimchi has gained international acclaim, finding its way onto menus and into grocery stores worldwide. It is revered for its complex flavors, nutritional value, and cultural significance.
In conclusion, the key subject of kimchi history reveals a rich tapestry of tradition, innovation, and cultural importance. From its humble origins as a preserved vegetable dish to its present-day status as a globally recognized delicacy, kimchi has evolved and adapted while remaining deeply embedded in Korean identity. Its enduring popularity speaks to its enduring legacy, as it continues to delight taste buds and bring people together around the world.
seo.call-to-action.title
seo.call-to-action.money-back
seo.call-to-action.message
1. When and where did kimchi originate?
Kimchi is a traditional Korean dish that has a long history and cultural significance in Korean cuisine. It is believed to have originated during the Three Kingdoms period in Korea, specifically in the 7th century. However, some sources suggest that the origins of kimchi can be traced back even earlier to the Baekje Kingdom in the 1st century AD. Kimchi was initially developed as a way to preserve vegetables during the harsh Korean winters when fresh produce was scarce. Over time, it evolved into a staple food in Korean households and became an integral part of Korean cuisine. The exact place of origin of kimchi is believed to be in the Korean peninsula, which includes present-day South and North Korea. Today, kimchi is enjoyed worldwide and is considered a cultural symbol of Korea.
2. What are the main ingredients used in making kimchi?
The main ingredients used in making kimchi, a traditional Korean fermented vegetable dish, are: 1. Napa cabbage: It is the primary vegetable used in kimchi, providing a crispy and crunchy texture. 2. Korean radish (mu): This radish is used for its mild and slightly sweet taste, adding a refreshing element to the kimchi. 3. Garlic: Fresh garlic cloves are mashed or minced and are an essential ingredient for flavoring the kimchi. 4. Ginger: Fresh ginger is grated or finely chopped and adds a subtle warmth and zing to the kimchi. 5. Red pepper flakes (gochugaru): This is a staple ingredient in kimchi, providing the characteristic spicy and tangy flavor. 6. Fish sauce or salted shrimp paste: These fermented seafood products are used to enhance the depth of flavor in kimchi. 7. Scallions (green onions): Chopped scallions add a savory and fresh taste to the kimchi. 8. Salt: It plays a crucial role in the fermentation process by drawing out moisture from the vegetables and creating an environment for the growth of beneficial bacteria. 9. Sugar: A small amount of sugar is sometimes added to balance the flavors and promote fermentation. 10. Other optional ingredients: Various vegetables like carrots, onion, and Asian chives can be added to further enhance the flavor and texture of the kimchi.
3. Are there different variations or types of kimchi?
Yes, there are indeed different variations and types of kimchi. Kimchi is a traditional Korean dish made by fermenting vegetables with various seasonings. While the most common type of kimchi is made with napa cabbage, there are numerous other varieties that use different vegetables as the main ingredient. Some well-known types of kimchi include: 1. Baechu Kimchi (Napa Cabbage Kimchi): This is the most popular and widely consumed type of kimchi. It is made with fermented napa cabbage, which is usually seasoned with spices, garlic, ginger, and chili pepper flakes. 2. Kkakdugi (Radish Kimchi): Kkakdugi is made with fermented radish cubes that are seasoned with similar ingredients as baechu kimchi. It has a crunchy texture and a slightly sweet and spicy taste. 3. Chonggak Kimchi (Ponytail Radish Kimchi): This variety of kimchi is made with small radishes, known as ponytail radishes, which have long green stems attached to them. It has a mild flavor and a slightly salty taste. 4. Oi Sobagi (Stuffed Cucumber Kimchi): Oi sobagi is made with cucumbers that are stuffed with a mixture of vegetables and seasonings. It has a refreshing and crunchy taste. 5. Gat Kimchi (Mustard Leaf Kimchi): Gat kimchi is made with mustard greens that are fermented with spices and chili pepper flakes. It has a slightly bitter and spicy flavor. These are just a few examples of the many types of kimchi available. Each variation has its own unique taste, texture, and preparation method, making kimchi a versatile and diverse dish.
4. Are there any specific health benefits associated with different types of kimchi?
Yes, different types of kimchi offer various health benefits due to their ingredients and fermentation process. Here are some examples: 1. Cabbage Kimchi: Cabbage kimchi, the most popular type, is low in calories and rich in vitamins A, C, and K. It is also a good source of fiber and contains beneficial bacteria that aid in digestion and support gut health. 2. Radish Kimchi: Radish kimchi, also known as Kkakdugi, is high in antioxidants and vitamin C. It can promote healthy skin, boost the immune system, and improve digestion due to its high fiber content. 3. Water Kimchi: Water kimchi, or mul kimchi, is made with a variety of vegetables soaked in a tangy brine. It is high in water content, providing hydration, and contains beneficial probiotics that support gut health. 4. White Kimchi: White kimchi, also known as baek kimchi, is made without chili peppers, resulting in a milder taste. It still offers health benefits such as improving digestion, promoting a healthy gut microbiome, and providing vitamins and minerals from its vegetable ingredients. 5. Kimchi made with additional ingredients: Some kimchi variations include ingredients like garlic, ginger, scallions, or fish sauce, which can add specific health benefits. Garlic and ginger are known for their anti-inflammatory properties, while scallions are rich in vitamin K and folate. Fish sauce provides protein and adds umami flavor. It's important to note that kimchi is typically high in sodium due to its fermentation process, so individuals with high blood pressure or sodium sensitivity should consume it in moderation. Also, homemade kimchi or those from reputable sources are recommended to ensure the quality and fermentation process.